By Greg Robinette, Director of ERP Services, Herdt Consulting, Inc.
Introduction
In the realm of data security, the protection of PII within the DoD presents unique challenges. Given the sensitivity of military operations and the personal safety of service members, the stakes for securing DoD PII are particularly high. This document outlines the distinctive types of PII encountered within the DoD and the risks associated with their compromise. It also emphasizes the importance of effective preventative measures, an active mitigation plan, and a well-designed and readily available recovery plan. The basic requirements for these measures and plans are included in an outline form.
Unique Types of DoD PII
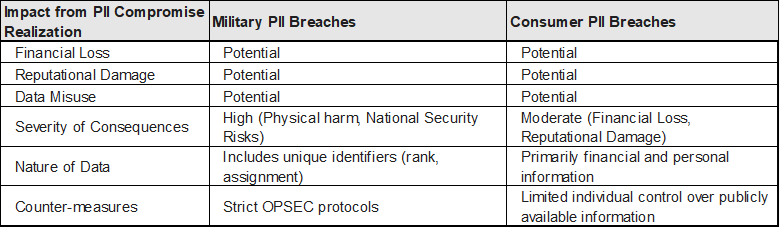
DoD PII goes beyond the standard consumer and employee data sets, incorporating a subset of data that includes military rank, skill specifications, command assignments, and locations. Such information, while crucial for operational integrity, could lead to unintended identification and exposure of personnel if mishandled.
Unique Risks Associated with DoD PII
While subject to the ‘standard’ risks all consumers face (when PII is compromised), the risks of DoD PII compromise include those same consumer risks plus a significant slate of additional risks. These DoD PII unique risks include:
Threat to Individuals:
- Targeted attacks: PII, such as home addresses, family information, and derived information (like family routines), can be used to target individuals through:
- Physical attacks: Knowing the location of a service member or their family could put them at risk of kidnapping or violence.
- Psychological warfare: Disclosing personal details publicly or sending threatening messages can be used to intimidate and demoralize personnel.
Disrupting Military Operations:
- Identifying key personnel: PII, such as names, ranks, and unit assignments, can be used to identify high-value targets (like commanding officers, intelligence specialists, logistics personnel, and other key operational people).
- Infiltrating communication networks: Correlation of public information with intercepted communications, combined with compromised PII, may yield insights into operational plans or force movements.
- Disinformation campaigns: Social media profiles and other publicly available data, combined with compromised PII, can be used to create fake accounts to spread misinformation, sow discord within the ranks, or manipulate public opinion.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities:
- Social engineering: Compromised PII details can be used to impersonate trusted individuals and gain access to sensitive information or systems.
- Targeting weaknesses: Information about an individual’s personal struggles or vulnerabilities could be used to coerce them into cooperating with potential or known opposition entities.
Important Considerations of DoD PII
- Publicly available information: Much of the data identified above may already be accessible through public sources like social media or government records.
- Counter-intelligence measures: Militaries extensively train personnel about operational security (OPSEC) to minimize the risk of exposing sensitive information.
Minimizing the Risk of PII Compromise in Technology and Information Systems
Many existing IT general or standard controls computing controls (ITGCC) facilitate protecting PII data. However, these controls alone may not be adequate for the task of protecting PII. They may not assure the greatest prevention or mitigation of all PII risks.
The following steps or tasks should be applied by all personnel responsible for the architecture and sustainment of systems that have PII data:
- Data Identification and Classification
- Identify and Classify PII – Conduct data discovery to identify and classify all forms of PII as outlined in DoD directives and guidelines. This involves understanding what data you have, where and how it is retained, and its sensitivity level.
- Access Control and Authorization
- Implement Least Privilege Access and Policies
- Ensure that access to PII is restricted to only those individuals who need it to perform their duties.
- Use role-based access controls to enforce the principle of least privilege.
- Apply these practices to all systems with production-level or actual PII data, including test systems and integration scenarios.
- User Authentication and Authorization
- Deploy strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify the identity of users accessing PII.
- Implement Least Privilege Access and Policies
- Data Encryption
- Encrypt Sensitive Data – This helps ensure that if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it remains unreadable and secure.
- Encrypt PII data at rest using strong encryption standards.
- Encrypt PII data in transit using strong encryption standards.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data – This helps ensure that if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it remains unreadable and secure.
- Data Minimization and Retention
- Minimize Data Collection
- Only collect PII that is necessary for the specified purpose and nothing more. This reduces the risk and impact of data breaches.
- Data Retention Policies
- Implement and enforce data retention policies that define how long PII should be kept and the procedures for its safe deletion or anonymization once it is no longer needed.
- Minimize Data Collection
- Incident Response and Reporting
- Develop an Incident Response Plan – Have a robust incident response plan in place.
- Include procedures for responding to data breaches involving PII.
- Include notification processes for affected individuals and reporting to relevant authorities.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan – Have a robust incident response plan in place.
- Training and Awareness
- Employee Training
- Regularly train employees on the importance of protecting PII, recognizing phishing attempts, and following security policies and procedures.
- Provide reports or status of organizational training supporting the protection of PII.
- Employee Training
- Regular Audits and Assessments
- Risk Assessments
- Execute initial and then regular risk assessments for the specific data classes that comprise PII or directly impact PII data.
- Perform security audits regularly to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with DoD requirements. This should include periodic reviews of access controls, encryption standards, and incident response plans.
- Risk Assessments
- Vendor and Third-Party Management
- Ensure Third-Party Compliance
- If you work with vendors or third parties that handle PII, ensure they comply with DoD PII protection requirements. This may involve conducting assessments or audits of third-party security practices.
- Assure that the initial collector of PII data knows all entities who receive the data or process the data.
- Ensure Third-Party Compliance
- Policy and Procedure Documentation
- Document Policies and Procedures
- Have clear, written policies and procedures outlining how PII will be handled, protected, and destroyed. Ensure these documents are accessible and understood by all relevant personnel.
- Assure that all policies meet or exceed all DoD directives and guidelines.
- Document Policies and Procedures
- Monitoring and Improvement
- Continuous Monitoring
- Provide processes, tools, and practices to monitor all systems, including third-party vendors.
- Provide regular reports on the status and results of the continuous monitoring.
- Regularly update security practices and technologies to address new threats.
- Continuous Improvement
- Review current practices and compare them to industry best practices. Adapt, adopt, and improve to ensure the highest quality PII protection.
- Continuous Monitoring
REMINDER – Focus on classified information. While PII can be dangerous, securing classified military information is the primary concern.
Conclusion
The safeguarding of DoD PII is a critical responsibility that requires diligence and attention at many levels. This document has outlined the unique challenges and risks associated with protecting DoD PII, highlighting the critical importance of implementing effective preventative measures, establishing robust mitigation strategies, and maintaining a comprehensive recovery plan. The exploration of the distinctive types of DoD PII, including military ranks, skill specifications, and command assignments, underscores the unique risks these data sets face—from targeted attacks and psychological warfare to the potential disruption of military operations and exploitation of vulnerabilities.
Minimizing the risk of PII compromise requires strict access control, data encryption, data minimization, and regular audits, among other strategies. These measures are essential to protect data crucial to service members’ personal safety and the operational integrity of military missions. The article points out the importance of continuous monitoring, regular training and awareness programs for employees, and the necessity of ensuring third-party compliance with DoD PII protection requirements.
The collective effort to protect DoD PII is not just a matter of operational security; it is a matter of national security. Each individual involved in handling DoD PII—from service members and government workers to civilian employees and contractors—plays a vital role in this endeavor. A shared commitment to implementing the outlined strategies and continuously adapting to emerging threats supports and increases the assurance of the safety and security of all DoD personnel and their critical missions.
Diligently safeguarding PII within the DoD both protects individuals and upholds the integrity and effectiveness of our military operations.
Reference information:Department of Defense Privacy Program Directive 5400.11
